how do glasses work physics
When the polarized sunglasses are put in front of your eyes the light gets filtered again. There are some more complicated systems as well but because they are expensive they are not as widely used.
It uses the slower speed of light in glass to its advantage by refracting the light twice.
. How the eye works is that natural lenses are able to bend the light that passes through. S M and L and they are responsible for identifying the colors blue green and red respectively. There are three types of cones.
Nearsighted corretion places virtual images of far objects on the retina. The surface of these lenses serves as our grating upon which the light will diffract. How do I know if my sunglasses are polarized in physics.
To put it very simply the eye gathers information and focuses the light through a lens to make an image - just like a camera. Our eyes detect colors using cones. Have you ever wondered friends how do glasses work physics.
Through the pupil light enters the eyes and gets focused by the lens into the retina. How do glasses work diagram. How does the eye change focus.
Lastly the crossed polarizing filters on the two lenses of the dorky glasses ensure that each eye sees only one of the images the one for that eye. A few different parts of the eye make this possible. But today in my blog I am going to explain to you why glasses.
Here in the picture above you can exactly see how this works. When you look through one of the lenses it should be very dark and you should see little to no glare but it will still look like the light is shining on the surface. For contacts which are much closer to the lens the size distortion is much less.
For glasses that correct for near sighted people this also means a reduction in size of the image on the retina. How do glasses use waves to work. Because of the different wavelengths of light each color is refracted a different amount.
Diffraction glasses like those we design at Rainbow Symphony work on this ancient principle of physics. The lens of the eye will need to compensate for closer objects. So making glasses is all about changing the focal length and point of focus so that the image goes directly onto the retina.
The polarized glasses allow only one of the images into each eye because each lens has a different polarization. A magnifying glass is usually a convex lens a lens that bulges outwards made of either glass or plastic. How do glasses work for myopia.
Then all the human physiology and brain processing power goes to work to analyze the differences between the images and create the effect of a three-dimensional image. Light hits the glass at an angle and it. The light from the sun oscillates in every direction.
The glasses allow only one of the images into each eye because they contain lenses with different polarization. When the light ray leaves the prism it speeds up again entering the air and refracts a second time. How do glasses work for farsightedness.
The blue cones usually operate disjointly whereas for most people the red and green cones might have working regions that overlap. One of the most common reasons for this is the abnormality in the shape of the eye. How Diffraction Glasses Work.
If the sunglasses are polarized you will notice the glare disappears. Many such questions are lingering in our minds. This is how normal eyes work.
First we produce a high-quality holographic lens that contains thousands of tiny lines. How do glasses work for nearsighted. Answers 1 Glasses are comprised of lenses that bend light.
When a beam of light passes through any curved piece of glass it has a tendency to either expand the beam and spread it out or make the beam narrower eventually into nothing then expand again. After the light of the sun got reflected by the surface of the water the light oscillates only in the horizontal orientation. However in some cases these light waves dont reach the retina correctly and it results in change in vision.

Physics Optics Lenses 1 Of 4 Converging Lens Youtube

How Corrective Lenses Work Eye Facts Computer Vision Syndrome Lenses
Physics Tutorial Refraction And The Ray Model Of Light
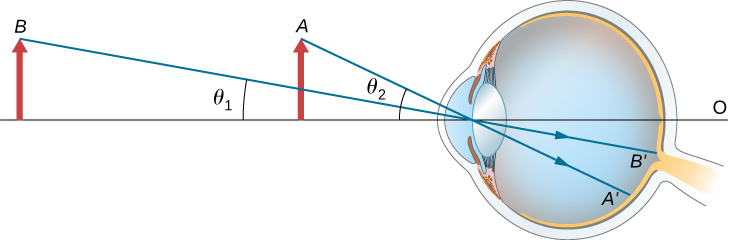
2 8 The Simple Magnifier Physics Libretexts
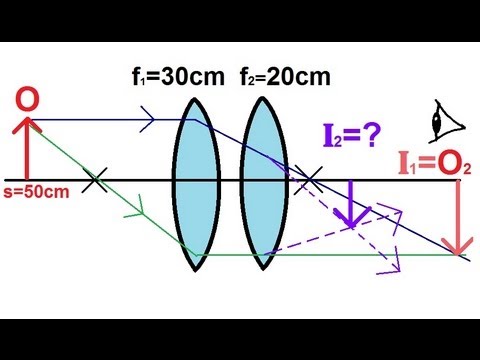
Physics Optics Lenses 1 Of 5 Lens Combinations Two Converging Lenses Youtube
Physics Tutorial Refraction And The Ray Model Of Light

Thin Lens Sign Conventions Article Khan Academy

Bent Out Of Shape Over Refraction
Physics Tutorial Refraction And The Ray Model Of Light

Thin Lens Sign Conventions Article Khan Academy

How To Get The Thinnest Lenses For Your Prescription Zenni Optical

Physics Optics Lenses Lens Combinations Converging Diverging Lenses 2

How Do Eyeglasses Work Infographic

Physics Optics Lenses Lens Combinations Converging Diverging Lenses 2


